Key Points:
- Melatonin for autistic adults may help improve sleep onset, duration, and overall sleep quality.
- Sleep issues in adults on the spectrum are linked to disruptions in circadian rhythms and sensory sensitivities.
- When used correctly, melatonin supplements can be part of a larger plan that includes behavioral strategies and professional support.
Sleep disturbances are common among autistic adults, often persisting from childhood into later life. In fact, research indicates that up to 83% of individuals with autism experience some form of sleep disorder. These issues—ranging from delayed sleep onset to nighttime awakenings—can deeply affect mental health, focus, and quality of life.
Because of this, many caregivers and individuals explore melatonin as a way to improve sleep naturally. This article dives into how melatonin works, its potential benefits, and key considerations for use in adults on the spectrum.
Does Melatonin Help Adults with Autism Sleep Better?
Yes, melatonin can help improve sleep quality in autistic adults by regulating the body’s internal clock and promoting faster sleep onset. Research has consistently shown that adults with autism often have irregular melatonin production, contributing to sleep onset delays and fragmented sleep cycles. Supplemental melatonin can help restore a more typical sleep pattern when paired with supportive routines.
Because autistic individuals frequently experience disruptions in their circadian rhythm, melatonin can help control this cycle. Supplementing it at the right time can encourage the body to settle into a more predictable sleep-wake rhythm.
Why Is Sleep Such a Struggle for Autistic Adults?
Sleep issues in autistic adults aren’t just minor inconveniences. They can seriously affect quality of life, worsening anxiety, sensory sensitivities, and emotional regulation. Autistic individuals often describe sleep as inconsistent, non-refreshing, or easily disrupted by environmental stimuli like light or sound.
There are several contributing factors that make sleep especially difficult:
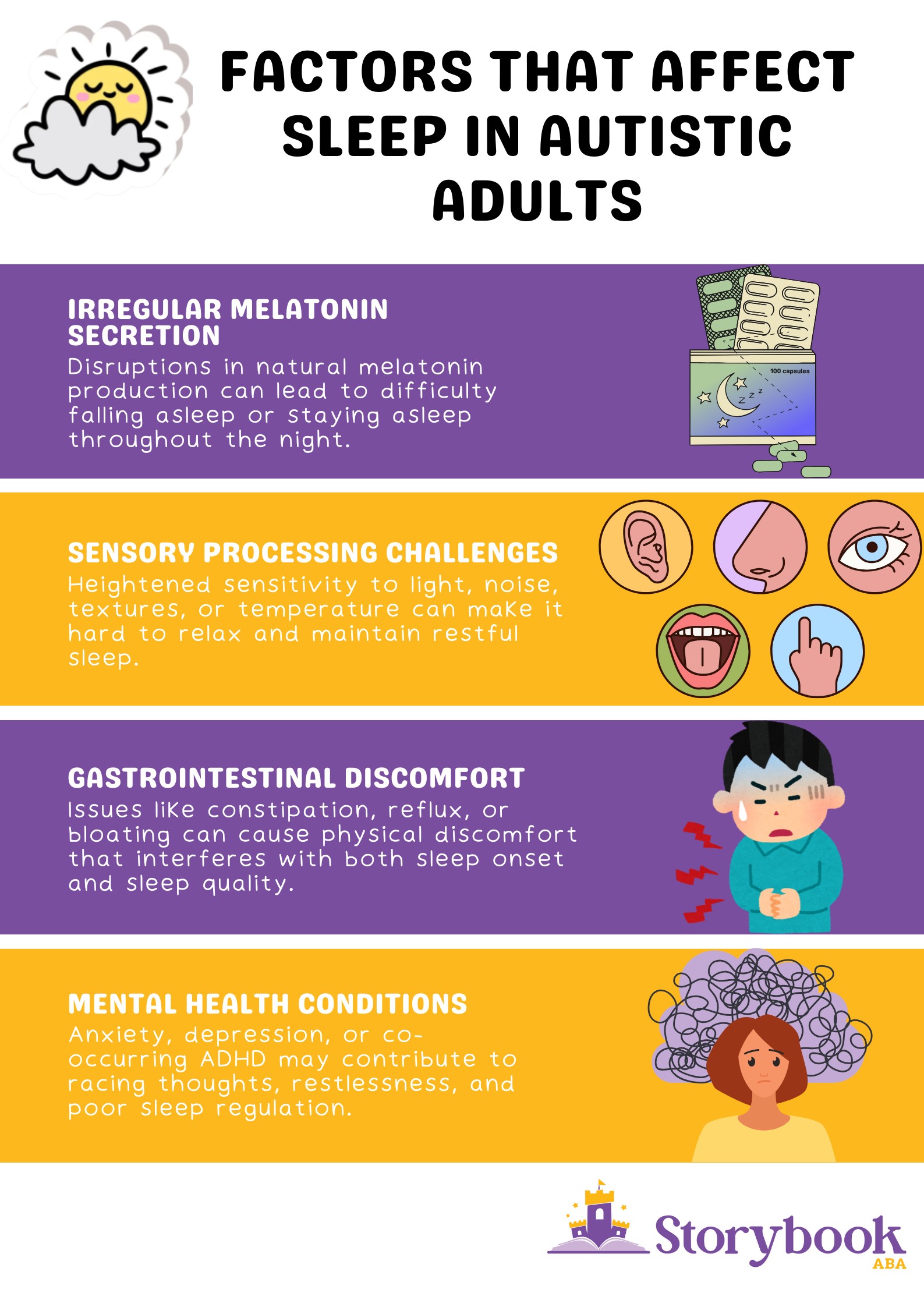
These factors make a compelling case for exploring melatonin use, especially when behavioral sleep interventions have only partial effects.
How Does Melatonin Work in the Body?
Melatonin is a hormone naturally made by the pineal gland when it gets dark. Its primary role is to help manage the body’s internal clock, also known as the circadian rhythm, which controls when we sleep and wake up.
In autistic individuals, studies have found reduced or delayed melatonin production, making it difficult to feel sleepy at the “right” time. Supplementing melatonin can mimic the body’s natural signal for sleep, especially when taken about 30–60 minutes before bedtime.
However, melatonin is not a sedative. It doesn’t force the body to sleep, but it encourages the conditions that make sleep more likely and more restful.
For those interested in supporting overall health alongside sleep, our article “Discover the Best Vitamins and Supplements That Support Autism” explores key nutrients that can enhance well-being and complement natural sleep aids like melatonin.
What Are the Key Benefits of Melatonin for Autistic Adults?
When used correctly, melatonin can improve more than just bedtime. It may help autistic adults feel more balanced, less irritable, and more alert during the day due to better nighttime rest.
Here are some of the most well-documented benefits:
1. Improved Sleep Onset
Autistic adults often struggle with delayed sleep onset due to irregular melatonin rhythms. Supplementing melatonin can help synchronize the body’s internal clock, making it easier to wind down and fall asleep naturally.
2. Longer Sleep Duration
Many autistic adults experience night terrors. Melatonin may help extend overall sleep time by reducing interruptions and promoting deeper, more restorative sleep throughout the night, which is essential for emotional and cognitive regulation.
3. Better Daytime Functioning
Poor sleep can heighten sensory sensitivities, irritability, and concentration issues. When melatonin supports better sleep, many autistic adults report feeling more focused, emotionally balanced, and better equipped to manage daily social or sensory demands.
4. Non-Habit Forming
Unlike certain prescription sleep aids, melatonin is not habit-forming and doesn’t lead to dependency or withdrawal. This makes it a safer choice for long-term use by those looking for steady, natural sleep support.
5. Fewer Side Effects
Melatonin is generally well-tolerated, with minimal side effects reported. Most users find it a gentler alternative to pharmaceutical sleep aids, which often come with risks like grogginess, dizziness, or dependency.
How Much Melatonin Should Autistic Adults Take?
There is no universal dosage for melatonin, especially for autistic individuals. Response varies widely, so it’s crucial to start low and adjust cautiously. Below are some general guidelines for taking melatonin:
- Start with a low dose: 0.5 to 1 mg about 30–60 minutes before bedtime
- Increase gradually: Only if no results are seen after a few days
- Maximum daily dose: Usually not exceeding 5 mg unless under medical supervision
- Formulations: Available in tablets, liquids, or time-release capsules
Always consult a physician before starting melatonin, especially if the person takes medications or has a history of seizures or other health issues.

What Are the Risks or Downsides of Using Melatonin?
Melatonin is widely considered safe for short- and long-term use in both children and adults. However, like any supplement, it is not completely without risk.
Here are some potential drawbacks:
1. Daytime Drowsiness or Grogginess
While melatonin supports nighttime sleep, some users—especially at higher doses—may feel tired or foggy the next morning. Adjusting the dose or timing can often reduce these lingering effects during the day.
2. Headaches or Vivid Dreams
Occasionally, melatonin can trigger side effects like headaches or unusually vivid dreams. These symptoms are typically mild and temporary, but it’s important to monitor how your body responds to the supplement.
3. Interaction with Other Medications
Melatonin may interact with medications such as blood thinners, antidepressants, or immune suppressants. Always consult a healthcare provider before adding melatonin to ensure it’s safe alongside any existing prescriptions.
4. Hormonal Effects
Since melatonin influences the body’s hormone regulation, long-term use could potentially impact reproductive hormones. Though rare, it’s wise to use the lowest effective dose and check in regularly with a healthcare professional.
Autistic adults who are sensitive to changes in routine or body sensations may also find melatonin’s effects uncomfortable at first. Monitoring and patience are key. For families exploring natural support options, our article “How Magnesium May Help Children on the Autism Spectrum” offers insights on how magnesium supplementation could provide calming benefits and support sensory regulation.
Can Melatonin Replace Behavioral Interventions?
No, melatonin should not replace behavioral strategies or therapy. While it can be an effective tool, long-term success in sleep improvement often requires changes in environment, routines, and habits.
In fact, melatonin works best when combined with:
- Consistent bedtime and wake-up routines
- Dimming lights and reducing screen use in the evening
- Avoiding caffeine and heavy meals before bed
- Using calming techniques like white noise or weighted blankets
Sleep is complex, especially in adults on the spectrum. Melatonin is one piece of the puzzle—not the entire solution.
What Alternatives or Adjuncts to Melatonin Are Available?
For autistic adults who don’t respond well to melatonin or need more support, several other options may help regulate sleep naturally. Below are some possible alternatives to melatonin for autistic adults:
- Magnesium: Calms the nervous system and supports deep sleep
- L-theanine: Promotes relaxation without sedation
- GABA supplements: Help ease overactive thoughts or anxiety
- CBD (cannabidiol): Some individuals report better sleep quality, though more research is needed
- Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I): Evidence-based, non-medication sleep support
Choosing an effective regimen depends on the individual’s medical history, sensitivities, and lifestyle factors. It’s best to involve healthcare professionals when exploring combinations.
Can ABA Therapy Assist with Sleeping Problems in Autistic Adults?
While melatonin addresses the biological side of sleep, behavioral support helps build sustainable habits. That’s where ABA therapy comes in. Applied Behavior Analysis can teach strategies to improve routines, reduce anxiety about bedtime, and support transitions from waking to sleeping states.
Sleep skills often don’t come naturally for autistic individuals—but they can be taught and strengthened over time. ABA therapists may use visual schedules, reinforcement strategies, and environmental modifications to make the bedtime process smoother and less stressful. When paired with melatonin, these changes can produce longer-lasting, more meaningful sleep improvements.
Get the Right Tools for Success with ABA Therapy
Melatonin for autistic adults can make a real difference—but it’s only part of a full picture of care. At Storybook ABA, we help individuals build sustainable routines and lifelong behavioral skills that support restful sleep and daily functioning.
If you’re navigating autism-related sleep challenges, let us help. We offer ABA therapy in Maryland and Virginia, tailored to the unique needs of autistic individuals across age groups. Whether you’re seeking support with daily routines, emotional regulation, or independence, our therapy teams are here to walk with you every step of the way.
Contact us today to learn how personalized ABA therapy can complement tools like melatonin and lead to brighter days and calmer nights.