Key Points:
- Hypertonia refers to an abnormal increase in muscle tone, which can be seen in individuals with autism.
- Individuals with autism who experience hypertonia may face challenges with movement, posture, and motor coordination.
- Early intervention, such as ABA therapy, can help manage motor difficulties and improve motor skills in children with autism.
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a condition that impacts the behavior, communication, and sensory processing skills of diagnosed individuals. One of these challenges includes motor difficulty, which is experienced by approximately 87% of autistic individuals.
A common example of a motor difficulty is hypertonia, which can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. Hypertonia and autism often intersect, complicating daily tasks and the development of motor skills.
In this article, we will explore hypertonia in autism, its symptoms, causes, and how it affects diagnosed individuals. We’ll also discuss practical strategies and therapeutic interventions that can help manage motor difficulties associated with hypertonia.
What is Hypertonia and How Does it Relate to Autism?
Hypertonia is a condition characterized by increased muscle tone, which can cause muscles to feel stiff, tight, or rigid. It is often associated with neurological disorders and can affect both voluntary and involuntary movements. In the context of autism, hypertonia is not always present, but it is more commonly observed in children who exhibit other motor challenges or developmental delays.
In individuals with autism, hypertonia can interfere with motor development and daily activities. These challenges may include difficulty in walking, sitting, standing, or controlling hand movements.
As autism often impacts motor coordination, hypertonia adds an additional layer of difficulty. For example, a child with autism and hypertonia may struggle with tasks such as eating, dressing, or playing due to muscle stiffness or reduced flexibility.
While hypertonia is not a core feature of autism, its presence in some individuals can make communication, social interactions, and other aspects of life more challenging.
What are the Symptoms of Hypertonia in Autism?
The symptoms of hypertonia in autism can vary significantly from person to person. These variations can present differently depending on the individual’s developmental stage and overall health. However, some common signs to watch for include:
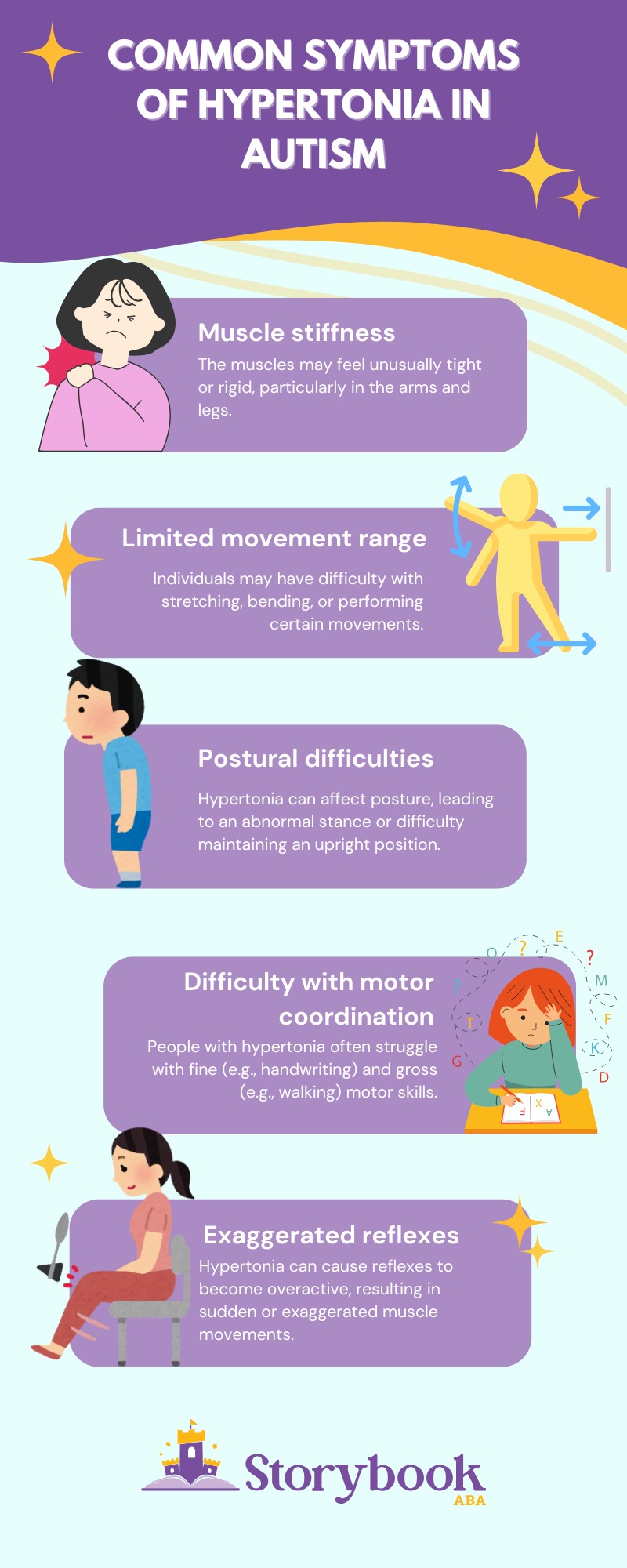
These symptoms can hinder the development of motor skills, making it harder for children to perform everyday tasks independently. In some cases, hypertonia can also lead to pain or discomfort due to the constant tension in the muscles.
4 Causes of Hypertonia in Autism
Hypertonia in autism can be caused by several factors, often related to underlying neurological or developmental differences. While the precise causes are not fully understood, some contributing factors may include:
1. Neurological Differences
Autism itself is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Differences in brain structure and function may contribute to motor impairments, such as hypertonia. Abnormalities in areas of the brain responsible for muscle control, such as the cerebellum, could lead to issues with motor coordination and muscle tone.
2. Cerebral Palsy
Some individuals with autism may also have cerebral palsy, a condition that affects muscle tone and movement. Cerebral palsy often results in muscle stiffness, spasms, and weakness, which may coexist with autism in some cases, leading to hypertonia.
3. Genetic Factors
Certain genetic mutations or conditions that influence muscle tone could also play a role in the development of hypertonia in individuals with autism. Genetic disorders like Rett syndrome and Fragile X syndrome, which are linked to autism, may also increase the likelihood of experiencing hypertonia.
4. Motor Dysfunction Due to Sensory Processing Challenges
Many individuals with autism experience sensory processing issues, which can affect how they respond to sensory stimuli. When a person is hypersensitive to touch or other sensory input, the body may react by tensing the muscles, which can contribute to hypertonia.
While these are potential causes of hypertonia in autism, it’s important to note that not every person with autism will experience hypertonia. Some individuals may show signs of low muscle tone (hypotonia) or typical muscle tone instead.
How Hypertonia Affect Daily Life in Autism
Hypertonia can have a significant impact on an individual’s ability to perform daily activities. For children with autism, the presence of hypertonia can make it difficult to develop essential motor skills such as sitting, walking, or eating. These motor challenges may cause frustration, anxiety, and a lack of independence.
Daily activities affected by hypertonia include:
1. Eating and Feeding
Hypertonia can make it difficult to use utensils or chew and swallow food properly, which may lead to feeding challenges. These difficulties can affect nutrition, mealtime independence, and overall enjoyment of eating.
2. Personal Care
Tasks like brushing teeth, combing hair, and getting dressed require fine motor skills that can be hindered by muscle stiffness. As a result, personal hygiene and daily routines may require extra time or assistance.
3. Mobility
Walking or running can become challenging due to the lack of flexibility in the muscles and joints. This can limit a person’s ability to move freely and participate in everyday activities.
4. Play and Recreation
Children with autism and hypertonia may find it difficult to participate in physical activities, such as running, jumping, or playing sports, due to muscle stiffness and coordination difficulties. These challenges can affect social interaction and overall engagement in play.
By understanding how hypertonia affects daily life, parents and caregivers can better support their child’s motor development and work toward increasing independence.
Managing Hypertonia in Autism: 4 Tips and Strategies
Although hypertonia can present challenges, there are several strategies and interventions that can help manage the condition and improve motor function. These approaches can also support emotional and cognitive development in children with autism. Some key strategies include:
1. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy (PT) is a key intervention for children with hypertonia. PT focuses on improving muscle strength, flexibility, and overall coordination. By engaging in specific exercises, children can increase their range of motion, reduce stiffness, and build strength.
Examples include:
- Stretching exercises to help reduce muscle tightness.
- Strengthening activities to help improve muscle function and coordination.
- Positioning techniques to help enhance posture and balance.
2. Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy (OT) helps children develop fine motor skills necessary for everyday tasks like dressing, eating, and writing. Occupational therapists may use a variety of tools and techniques to improve hand-eye coordination and motor planning.
3. Medication
In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications to help relax the muscles and reduce spasticity. These medications may include muscle relaxants, which can temporarily reduce stiffness and improve mobility. However, medication is typically used in conjunction with other therapies and should be managed under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
4. ABA Therapy
ABA therapy (Applied Behavior Analysis) can play a critical role in managing hypertonia by helping individuals with autism develop motor skills in a structured and supportive environment. ABA therapy activities can help break down complex tasks into manageable steps, providing clear guidance on how to perform activities with increased independence. It can also incorporate positive reinforcement strategies to encourage progress.
If you’re interested in how physical symptoms like hypertonia relate to autism, you may also want to read our article, “Night Terrors in Autism: Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions.” It explores another challenging aspect that can significantly impact sleep and overall well-being in individuals on the spectrum.
Start Your Child’s Journey to Success with ABA Therapy
Storybook ABA offers specialized ABA therapy for children with autism, including those who experience hypertonia. Our team works with families in Maryland and Virginia to create customized treatment plans that address motor difficulties, improve behavior, and promote independence.
By incorporating ABA therapy, we help children with autism overcome motor challenges and build the skills they need to succeed in daily life. Our team of experienced professionals is here to support your child’s growth and development.
Contact us today to learn more about ABA therapy in Maryland and Virginia, and discover how we can assist in improving your child’s motor skills, independence, and quality of life.